1. 데이터 바인딩
- 두 개의 데이터/ 정보에 대한 소스를 결합하고 데이터 동기화를 유지하는 기술
- source와 destination UI 구성간에 바인딩을 주로 함
- {Binding} 이렇게 중괄호 사이에 넣어서 사용
[예제]
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.HelloBoundWorldSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="HelloBoundWorldSample" Height="110" Width="280">
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBox Name="txtValue" />
<WrapPanel Margin="0,10">
<TextBlock Text="Value: " FontWeight="Bold" />
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Path=Text, ElementName=txtValue}" />
</WrapPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Window>[결과]
- TextBox의 Name을 txtValue로 설정
- TextBlock의 Text에 바인딩을 시킴 => Binding Path를 Text로 연결 + ElementName을 txtValue로 설정
=> TextBlock의 Text가 현재 바인딩 하고 있는 TextBox에 사용자가 적은 Text가 그대로 연결되어 나옴

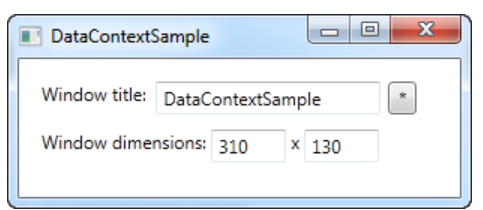
1-1. DataContext
- 바인딩의 기본 소스
- 기본 설정값은 따로 없음(모두 null 값을 가짐)
[예제]
1) XAML
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.DataContextSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="DataContextSample" Height="130" Width="280">
<StackPanel Margin="15">
<WrapPanel>
<TextBlock Text="Window title: " />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Title, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" Width="150" />
</WrapPanel>
<WrapPanel Margin="0,10,0,0">
<TextBlock Text="Window dimensions: " />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Width}" Width="50" />
<TextBlock Text=" x " />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Height}" Width="50" />
</WrapPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Window>2) Code-Behind
using System;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding
{
public partial class DataContextSample : Window
{
public DataContextSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
// DataContext의 내용을 자기자신의 내용으로 함
this.DataContext = this;
}
}
}3) 결과
- 첫번째 WrapPanel의 TextBox의 Text는 Title에 연결됨
- 두번째 WrapPanel의 첫번째 TextBox의 Text는 Width에 연결되고 두번째 TextBox의 Text는 Height에 연결됨
- Code-Behind에서 Context의 내용은 자기자신으로 정의하였으므로, 각 Title과 Width, Height는 자기자신의 것과 연결되어 화면에 자기자신의 Title, Width, Height가 보여지게 된다.

1-2. Code-Behind로 바인딩
- Binding 인스턴스를 만들어 작동 -> 생성자에서 직접 원하는 경로를 지정
(ex) Binding b = new Binding("Text");
- 소스를 지정해야 함(바인딩 할 대상)
- 실제 연결 -> SetBinding 이용 -> 바인딩하는 자신의 속성과 바인딩 인스턴스를 매개 변수로 받음
[예제]
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.CodeBehindBindingsSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="CodeBehindBindingsSample" Height="110" Width="280">
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBox Name="txtValue" />
<WrapPanel Margin="0,10">
<TextBlock Text="Value: " FontWeight="Bold" />
<TextBlock Name="lblValue" />
</WrapPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding
{
public partial class CodeBehindBindingsSample : Window
{
public CodeBehindBindingsSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
Binding binding = new Binding("Text"); // 바인딩 인스턴스 생성
binding.Source = txtValue; // 소스 연결
lblValue.SetBinding(TextBlock.TextProperty, binding); // 실제 바인딩
}
}
}3) 결과
- Text 속성의 바인딩 인스턴스 생성
- TextBox txtValue를 소스로 연결
- TextBlock lblValue에 바인딩

1-3. UpdateSourceTrigger 속성
- 변경된 내용이 반영되는 것을 조절함
- Defult가 기본값, 다른 옵션들로는 PropertyChanged, LostFocus, Explicit 이 있음
[예제]
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.DataContextSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="DataContextSample" Height="130" Width="310">
<StackPanel Margin="15">
<WrapPanel>
<TextBlock Text="Window title: " />
<TextBox Name="txtWindowTitle" Text="{Binding Title, UpdateSourceTrigger=Explicit}" Width="150" />
<Button Name="btnUpdateSource" Click="btnUpdateSource_Click" Margin="5,0" Padding="5,0">*</Button>
</WrapPanel>
<WrapPanel Margin="0,10,0,0">
<TextBlock Text="Window dimensions: " />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Width, UpdateSourceTrigger=LostFocus}" Width="50" />
<TextBlock Text=" x " />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Height, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" Width="50" />
</WrapPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding
{
public partial class DataContextSample : Window
{
public DataContextSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.DataContext = this;
}
private void btnUpdateSource_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 버튼을 누르면 값이 적용되도록 함
BindingExpression binding = txtWindowTitle.GetBindingExpression(TextBox.TextProperty);
binding.UpdateSource();
}
}
}3) 결과
- 첫번째 Title은 Explicit으로 설정 -> 직접 업데이트를 수행하지 않으면 내용이 변경되지 않음(버튼을 누르면 변경됨)
- 두번째 Width는 LostFocus로 설정 -> 포커스가 바뀔 때마다 값이 없데이트 됨
- 세번째 Height는 PropertyChanged로 설정 -> 바인딩 속성이 변경될 때마다 즉시 변경됨
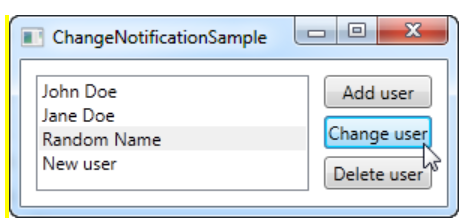
1-4. ObservableCollection, INotifyPropertyChanged
[ObservableCollection<T>]
- List<T> 와 역할은 거의 유사
- INotify~ 이렇게 생긴 인터페이스가 상속된 개체들에 변화가 생기면 UI에 알려주어 자동으로 업데이트 시켜줌
[예제]
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.ChangeNotificationSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="ChangeNotificationSample" Height="135" Width="300">
<DockPanel Margin="10">
<StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Right" Margin="10,0,0,0">
<Button Name="btnAddUser" Click="btnAddUser_Click">Add user</Button>
<Button Name="btnChangeUser" Click="btnChangeUser_Click" Margin="0,5">Change user</Button>
<Button Name="btnDeleteUser" Click="btnDeleteUser_Click">Delete user</Button>
</StackPanel>
<ListBox Name="lbUsers" DisplayMemberPath="Name"></ListBox>
</DockPanel>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding
{
public partial class ChangeNotificationSample : Window
{
//private List<User> users = new List<User>() // -> UI 갱신이 안됨 -> ObservableCollection 사용
private ObservableCollection<User> users = new ObservableCollection<User>();
public ChangeNotificationSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
users.Add(new User() { Name = "John Doe" });
users.Add(new User() { Name = "Jane Doe" });
lbUsers.ItemsSource = users;
}
private void btnAddUser_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
users.Add(new User() { Name = "New user" });
}
private void btnChangeUser_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 선택된 아이템이 있는 경우에만 동작 -> 선택 아이템의 이름 변경
if(lbUsers.SelectedItem != null)
(lbUsers.SelectedItem as User).Name = "Random Name";
}
private void btnDeleteUser_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 선택된 아이템이 있는 경우에만 동작 -> 선택 아이템 삭제
if(lbUsers.SelectedItem != null)
users.Remove(lbUsers.SelectedItem as User);
}
}
public class User : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string name;
public string Name {
get { return this.name; }
set
{
if(this.name != value)
{
this.name = value;
this.NotifyPropertyChanged("Name");
}
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public void NotifyPropertyChanged(string propName)
{
if(this.PropertyChanged != null)
this.PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propName));
}
}
}3) 결과
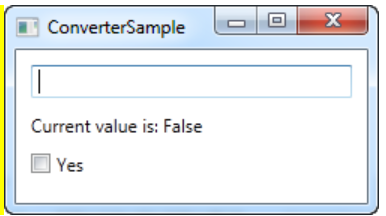
1-5. 값 변환
- 호환되지 않는 데이터를 바인딩 시켜야 할 경우 사용
- 예를 들어, 파일의 크기에 따라 바이트, 킬로바이트, 메가이트 등 단위로 나워 표시 할 경우 또는 체크박스를 값으로 확인하려는데 값이 Boolean 값이 아니라 "yes" "no" 처럼 문자열인 경우 등이 있다.
[예제]
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.ConverterSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding"
Title="ConverterSample" Height="140" Width="250">
<Window.Resources>
<local:YesNoToBooleanConverter x:Key="YesNoToBooleanConverter" />
</Window.Resources>
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBox Name="txtValue" />
<WrapPanel Margin="0,10">
<TextBlock Text="Current value is: " />
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=txtValue, Path=Text, Converter={StaticResource YesNoToBooleanConverter}}"></TextBlock>
</WrapPanel>
<CheckBox IsChecked="{Binding ElementName=txtValue, Path=Text, Converter={StaticResource YesNoToBooleanConverter}}" Content="Yes" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Data;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding
{
public partial class ConverterSample : Window
{
public ConverterSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
public class YesNoToBooleanConverter : IValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, System.Globalization.CultureInfo culture)
{
switch(value.ToString().ToLower())
{
case "yes":
return true;
case "no":
return false;
}
return false;
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, System.Globalization.CultureInfo culture)
{
if(value is bool)
{
if((bool)value == true)
return "yes";
else
return "no";
}
return "no";
}
}
}3) 결과
- 문자열을 이용해 체크박스의 값을 변경시키위해 값 변환 IValueConverter를 사용하였다.
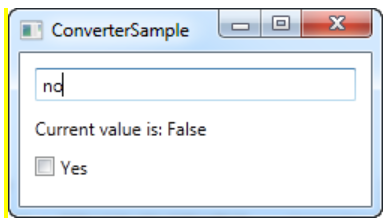
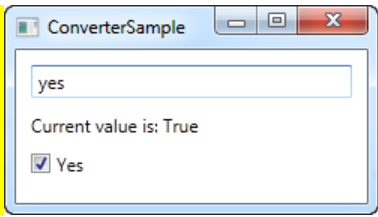
1-6. StringFormat property
- 특정 값이 표시되는 방식만 변경하고 다른 유형으로는 변환할 필요가 없는 경우 사용
- 유연성이 다소 떨어지지만 사용이 간편함
[예제]
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.DataBinding.StringFormatSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
<!-- 추가해야함-->
xmlns:system="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib"
Title="StringFormatSample" Height="150" Width="250"
Name="wnd">
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=wnd, Path=ActualWidth, StringFormat=Window width: {0:#,#.0}}" />
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=wnd, Path=ActualHeight, StringFormat=Window height: {0:C}}" />
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Source={x:Static system:DateTime.Now}, StringFormat=Date: {0:dddd, MMMM dd}}" />
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Source={x:Static system:DateTime.Now}, StringFormat=Time: {0:HH:mm}}" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>[결과]
- 첫번째, 두번째는 StringFormat이 Window의 너비와 높이를 바인딩하였고, 형식 문자열을 사용해 출력하였다.
- 세번째, 네번째는 현재 날짜를 가져와 각각 날짜와 시간에 바인딩하여 각각의 형식대로 출력하였다.
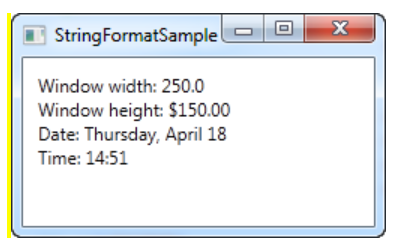
2. 커맨드
- 편의성을 위해 쓰는 단축키를 사용할 수 있다.
[예제 1]
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.Commands.UsingCommandsSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="UsingCommandsSample" Height="100" Width="200">
<Window.CommandBindings>
<CommandBinding Command="ApplicationCommands.New" Executed="NewCommand_Executed" CanExecute="NewCommand_CanExecute" />
</Window.CommandBindings>
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center">
<Button Command="ApplicationCommands.New">New</Button>
</StackPanel>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.Commands
{
public partial class UsingCommandsSample : Window
{
public UsingCommandsSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void NewCommand_CanExecute(object sender, CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 아무 동작도 하지 않을 때 특정 커맨드가 사용 가능한지 여부
e.CanExecute = true;
}
private void NewCommand_Executed(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
//커맨드가 발동했을 때 동작
MessageBox.Show("The New command was invoked");
}
}
}3) 결과
- New 버튼을 눌렀을 때 메세지 창이 뜸
- ApplicationCommands.New이므로 커맨드 버튼인 Ctrl+N을 눌렀을 때도 같은 메세지 창이 뜸
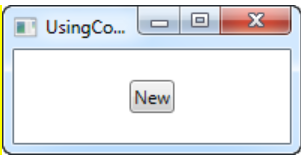
[예제 2]
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.Commands.CommandCanExecuteSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="CommandCanExecuteSample" Height="200" Width="250">
<Window.CommandBindings>
<CommandBinding Command="ApplicationCommands.Cut" CanExecute="CutCommand_CanExecute" Executed="CutCommand_Executed" />
<CommandBinding Command="ApplicationCommands.Paste" CanExecute="PasteCommand_CanExecute" Executed="PasteCommand_Executed" />
</Window.CommandBindings>
<DockPanel>
<WrapPanel DockPanel.Dock="Top" Margin="3">
<Button Command="ApplicationCommands.Cut" Width="60">_Cut</Button>
<Button Command="ApplicationCommands.Paste" Width="60" Margin="3,0">_Paste</Button>
</WrapPanel>
<TextBox AcceptsReturn="True" Name="txtEditor" />
</DockPanel>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.Commands
{
public partial class CommandCanExecuteSample : Window
{
public CommandCanExecuteSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void CutCommand_CanExecute(object sender, CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 단어가 있고, 해당 단어가 선택된 경우에만 동작
e.CanExecute = (txtEditor != null) && (txtEditor.SelectionLength > 0);
}
private void CutCommand_Executed(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
txtEditor.Cut();
}
private void PasteCommand_CanExecute(object sender, CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
e.CanExecute = Clipboard.ContainsText();
}
private void PasteCommand_Executed(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
txtEditor.Paste();
}
}
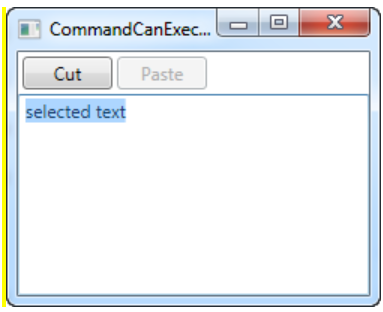
}3) 결과
- 단어가 있고, 해당 단어를 아래 그림처럼 드래그해서 선택했을 경우에만 Cut버튼이나 커맨드 키인 Ctrl+X로 동작한다.
- Paste는 Cut한 단어가 있을 경우에만 동작한다.
[예제 3]
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.Commands.CommandsWithCommandTargetSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="CommandsWithCommandTargetSample" Height="200" Width="250">
<DockPanel>
<WrapPanel DockPanel.Dock="Top" Margin="3">
<Button Command="ApplicationCommands.Cut" CommandTarget="{Binding ElementName=txtEditor}" Width="60">_Cut</Button>
<Button Command="ApplicationCommands.Paste" CommandTarget="{Binding ElementName=txtEditor}" Width="60" Margin="3,0">_Paste</Button>
</WrapPanel>
<TextBox AcceptsReturn="True" Name="txtEditor" />
</DockPanel>
</Window>[결과]
- 바인딩을 이용해 Code-behind 작성 없이 예제2와 같은 기능을 구현했다.
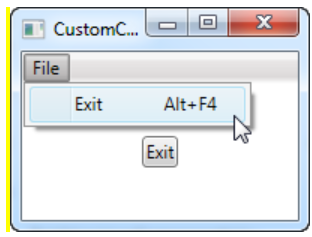
[예제 4] 커스텀 커맨드
1) xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.Commands.CustomCommandSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:self="clr-namespace:WpfTutorialSamples.Commands"
Title="CustomCommandSample" Height="150" Width="200">
<Window.CommandBindings>
<CommandBinding Command="self:CustomCommands.Exit" CanExecute="ExitCommand_CanExecute" Executed="ExitCommand_Executed" />
</Window.CommandBindings>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Menu>
<MenuItem Header="File">
<MenuItem Command="self:CustomCommands.Exit" />
</MenuItem>
</Menu>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="1" HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center">
<Button Command="self:CustomCommands.Exit">Exit</Button>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Window>2) code-behind
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.Commands
{
public partial class CustomCommandSample : Window
{
public CustomCommandSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void ExitCommand_CanExecute(object sender, CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
e.CanExecute = true;
}
private void ExitCommand_Executed(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
Application.Current.Shutdown();
}
}
public static class CustomCommands
{
public static readonly RoutedUICommand Exit = new RoutedUICommand
(
"Exit", "Exit", typeof(CustomCommands),
new InputGestureCollection()
{
// alt+F4 라는 새로운 커맨드 등록
new KeyGesture(Key.F4, ModifierKeys.Alt)
}
);
//Define more commands here, just like the one above
}
}3) 결과
- 직접 설정한 커맨드를 이용할 수 있다.