1. XAML 이벤트 - 마우스 이벤트
- MouseUp : 마우스를 놓을 때 발생
- MouseDown : 마우스를 누를 때 발생
- 이벤트를 생성하는 2가지 방법
1) XAML에서 직접 호출
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.XAML.EventsSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="EventsSample" Height="300" Width="300">
<Grid Name="pnlMainGrid" MouseUp="pnlMainGrid_MouseUp" Background="LightBlue">
// 1) 위처럼 MouseUp의 델리게이트를 직접 연결해줌
</Grid>
</Window>2) Code-behind에서 델리게이트 추가
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.XAML
{
public partial class EventsSample : Window
{
public EventsSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 2) Code-behind에서 델리게이트에 직접 추가함
pnlMainGrid.MouseUp += new MouseButtonEventHandler(pnlMainGrid_MouseUp);
}
// MouseUp 이벤트 발생시 호출되는 함수
private void pnlMainGrid_MouseUp(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("You clicked me at " + e.GetPosition(this).ToString());
}
}
}
2. Window
- 원도우의 뼈대인 경계선, 타이틀 바, 최대화 및 최소화, 닫기 버튼을 제공한다.
- XAML(.xaml) 파일과 CodeBehind(.cs)로 구성되어 있다.
- x:Class 속성은 XAML 파일에게 어떤 클래스를 이용하는지 알려준다.
1) 시작 XAML
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Window1" Height="300" Width="300">
<Grid>
</Grid>
</Window>2) 시작 CodeBehind
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
//…more using statements
namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for Window1.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class Window1 : Window
{
public Window1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
}
3. WPF app
- 솔루션 탐색기를 찾아보면 App.xaml과 App.xaml.cs파일이 들어있다.(이걸 몰라서 찾는데 한참 걸렸다..ㅋㅋ)
- StartUri 속성 : 어플리케이션이 실행될 때 어떤 윈도우 또는 페이지로 시작하는지 정의하는 부분이다.
- 아래 코드처럼 Application_Startup 이벤트를 StartUri에 넣으면 CodeBehind에서 정의한 이벤트를 거쳐 윈도우가 생성된다.
<Application x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.App"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Startup="Application_Startup"> // Application_Startup 이벤트
<Application.Resources></Application.Resources>
</Application>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples
{
public partial class App : Application
{
private void Application_Startup(object sender, StartupEventArgs e)
{
// startup 윈도우를 생성
MainWindow wnd = new MainWindow();
// 윈도우의 타이틀을 변경
wnd.Title = "Something else";
// 윈도우를 보여줌
wnd.Show();
}
}
}
4. 리소스
- 데이터를 리소스 형태로 저장할 수 있음
1) 문자열 저장(Static)
- XAML
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.WPF_Application.ResourceSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:sys="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib"
Title="ResourceSample" Height="150" Width="350">
<Window.Resources>
// strHelloWorld에 "Hello, world!"가 저장됨
<sys:String x:Key="strHelloWorld">Hello, world!</sys:String>
</Window.Resources>
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBlock Text="{StaticResource strHelloWorld}" FontSize="56" />
<TextBlock>Just another "<TextBlock Text="{StaticResource strHelloWorld}" />" example, but with resources!</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Window>2) 콤보박스 만들기
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.WPF_Application.ExtendedResourceSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:sys="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib"
Title="ExtendedResourceSample" Height="160" Width="300"
Background="{DynamicResource WindowBackgroundBrush}">
<Window.Resources>
<sys:String x:Key="ComboBoxTitle">Items:</sys:String>
<x:Array x:Key="ComboBoxItems" Type="sys:String">
<sys:String>Item #1</sys:String>
<sys:String>Item #2</sys:String>
<sys:String>Item #3</sys:String>
</x:Array>
<LinearGradientBrush x:Key="WindowBackgroundBrush">
<GradientStop Offset="0" Color="Silver"/>
<GradientStop Offset="1" Color="Gray"/>
</LinearGradientBrush>
</Window.Resources>
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<Label Content="{StaticResource ComboBoxTitle}" />
<ComboBox ItemsSource="{StaticResource ComboBoxItems}" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>3) Code-behind에서 리소스 접근
- Application
<Application x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.App"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:sys="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib"
StartupUri="WPF application/ResourcesFromCodeBehindSample.xaml">
<Application.Resources>
// Application 리소스
<sys:String x:Key="strApp">Hello, Application world!</sys:String>
</Application.Resources>
</Application>- Window
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.WPF_Application.ResourcesFromCodeBehindSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:sys="clr-namespace:System;assembly=mscorlib"
Title="ResourcesFromCodeBehindSample" Height="175" Width="250">
<Window.Resources>
// Window 리소스
<sys:String x:Key="strWindow">Hello, Window world!</sys:String>
</Window.Resources>
<DockPanel Margin="10" Name="pnlMain">
<DockPanel.Resources>
// Panel 리소스
<sys:String x:Key="strPanel">Hello, Panel world!</sys:String>
</DockPanel.Resources>
<WrapPanel DockPanel.Dock="Top" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="10">
<Button Name="btnClickMe" Click="btnClickMe_Click">Click me!</Button>
</WrapPanel>
<ListBox Name="lbResult" />
</DockPanel>
</Window>- Code-behind
using System;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.WPF_Application
{
public partial class ResourcesFromCodeBehindSample : Window
{
public ResourcesFromCodeBehindSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnClickMe_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 각기 접근 방식이 다름 //
// Window 내부의 Panel 리소스
lbResult.Items.Add(pnlMain.FindResource("strPanel").ToString());
// Window 리소스
lbResult.Items.Add(this.FindResource("strWindow").ToString());
// Application 리소스
lbResult.Items.Add(Application.Current.FindResource("strApp").ToString());
}
}
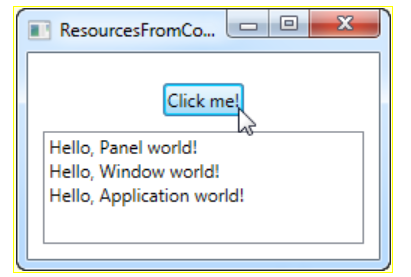
}- 결과창(3번 클릭했을시)
5. 예외처리
- 로컬에서는 보통 try-catch 문으로 처리함
- WPF에서는 Applicaiont 클래스의 DispatcherUnhandledException 이벤트를 추가하여 전역으로 예외처리가 가능
1) try-catch 이용
<Window x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.WPF_Application.ExceptionHandlingSample"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="ExceptionHandlingSample" Height="200" Width="200">
<Grid>
<Button HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" Click="Button_Click">
Do something bad!
</Button>
</Grid>
</Window>using System;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples.WPF_Application
{
public partial class ExceptionHandlingSample : Window
{
public ExceptionHandlingSample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
string s = null;
try
{
s.Trim();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("A handled exception just occurred: " + ex.Message, "Exception Sample", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Warning);
}
s.Trim(); // 처리되지 않음
}
}
}
2) Applicaiont 클래스의 DispatcherUnhandledException 이용
<Application x:Class="WpfTutorialSamples.App"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
DispatcherUnhandledException="Application_DispatcherUnhandledException"
StartupUri="WPF Application/ExceptionHandlingSample.xaml">
<Application.Resources>
</Application.Resources>
</Application>using System;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfTutorialSamples
{
public partial class App : Application
{
private void Application_DispatcherUnhandledException(object sender, System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("An unhandled exception just occurred: " + e.Exception.Message, "Exception Sample", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Error);
e.Handled = true;
}
}
}

